Page 36 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 36
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
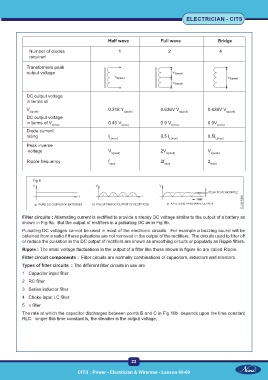
Half wave Full wave Bridge
Number of diodes 1 2 4
required
Transformers peak
output voltage
DC output voltage
in terms of
V s(peak) 0.318 Y s(peak) 0.636V V s(peak) 0.636V V s(peak)
DC output voltage
in terms of V 0.45 V 0.9 V 0.9V
s(rms) s(rms) s(rms) s(rms)
Diode current
rating I L(max) 0.5 I L(max) 0.5I L(max)
Peak inverse
voltage V s(peak) 2V s(peak) V s(peak)
Ripple frequency f input 2f input 2 finput
Fig 8
Filter circuits : Alternating current is rectified to provide a steady DC voltage similar to the output of a battery as
shown in Fig 9a. But the output of rectifiers in a pulsating DC as in Fig 9b.
Pulsating DC voltages cannot be used in most of the electronic circuits. For example a buzzing sound will be
obtained from a radio if these pulsations are not removed in the output of the rectifiers. The circuits used to filter off
or reduce the pulsation in the DC output of rectifiers are known as smoothing circuits or popularly as Ripple filters.
Ripple : The small voltage fluctuations in the output of a filter like those shown in figure 9c are called Ripple.
Filter circuit components : Filter circuits are normally combinations of capacitors, inductors and resistors.
Types of filter circuits : The different filter circuits in use are
1 Capacitor input filter.
2 RC filter
3 Series inductor filter
4 Choke input LC filter
5 p filter.
The rate at which the capacitor discharges between points B and C in Fig 10b depends upon the time constant
RLC. longer this time constant is, the steadier is the output voltage.
23
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69