Page 41 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 41
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
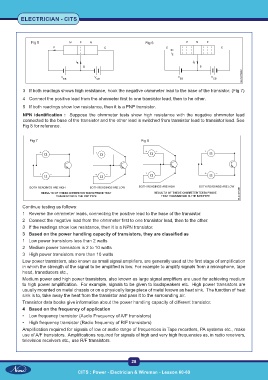
Fig 5 Fig 6
3 If both readings shows high resistance, hook the negative ohmmeter lead to the base of the transistor. (Fig 7)
4 Connect the positive lead from the ohmmeter first to one transistor lead, then to he other.
5 If both readings show low resistance, then it is a PNP transistor.
NPN identification : Suppose the ohmmeter tests show high resistance with the negative ohmmeter lead
connected to the base of the transistor and the other lead is switched from transistor lead to transistor lead. See
Fig 8 for reference.
Fig 7 Fig 8
Continue testing as follows:
1 Reverse the ohmmeter leads, connecting the positive lead to the base of the transistor.
2 Connect the negative lead from the ohmmeter first to one transistor lead, then to the other.
3 If the readings show low resistance, then it is a NPN transistor.
3 Based on the power handling capacity of transistors, they are classified as
1 Low power transistors less than 2 watts
2 Medium power transistors is 2 to 10 watts
3 High power transistors more than 10 watts
Low power transistors, also known as small signal amplifiers, are generally used at the first stage of amplification
in which the strength of the signal to be amplified is low. For example to amplify signals from a microphone, tape
head, transducers etc.,
Medium power and high power transistors, also known as large signal amplifiers are used for achieving medium
to high power amplification. For example, signals to be given to loudspeakers etc. High power transistors are
usually mounted on metal chassis or on a physically large piece of metal known as heat sink. The function of heat
sink is to, take away the heat from the transistor and pass it to the surrounding air.
Transistor data books give information about the power handling capacity of different transistor.
4 Based on the frequency of application
• Low frequency transistor (Audio Frequency of A/F transistors)
• High frequency transistor (Radio frequency of R/F transistors)
Amplification required for signals of low or audio range of frequencies in Tape recorders, PA systems etc., make
use of A/F transistors. Amplifications required for signals of high and very high frequencies as, in radio receivers,
television receivers etc., use R/F transistors.
28
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69