Page 34 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 34
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
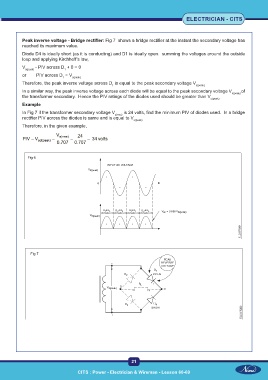
Peak inverse voltage - Bridge rectifier: Fig 7 shows a bridge rectifier at the instant the secondary voltage has
reached its maximum value.
Diode D4 is ideally short (as it is conducting) and D1 is ideally open. summing the voltages around the outside
loop and applying Kirchhoff’s law,
V s(peak) - PIV across D + 0 = 0
1
or PIV across D = V s(peak)
1
Therefore, the peak inverse voltage across D is equal to the peak secondary voltage V
1 s(peak)
In a similar way, the peak inverse voltage across each diode will be equal to the peak secondary voltage V s(peak) of
the transformer secondary. Hence the PIV ratings of the diodes used should be greater than V s(peak)
Example
In Fig 7 if the transformer secondary voltage V s(rms) is 24 volts, find the minimum PIV of diodes used. In a bridge
rectifier PIV across the diodes is same and is equal to V s(peak)
Therefore, in the given example,
Fig 6
Fig 7
21
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 60-69