Page 107 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 107
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
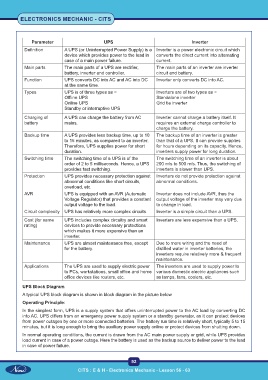
Parameter UPS Inverter
Definition A UPS (or Uninterrupted Power Supply) is a Inverter is a power electronic circuit which
device which provides power to the load in converts the direct current into alternating
case of a main power failure. current.
Main parts The main parts of a UPS are rectifier, The main parts of an inverter are inverter
battery, inverter and controller. circuit and battery.
Function UPS converts DC into AC and AC into DC Inverter only converts DC into AC.
at the same time.
Types UPS is of three types as − Inverters are of two types as −
Offline UPS Standalone inverter
Online UPS Grid tie inverter
Standby or interruptive UPS
Charging of A UPS can charge the battery from AC Inverter cannot charge a battery itself. It
battery mains. requires an external charge controller to
charge the battery.
Backup time A UPS provides less backup time, up to 10 The backup time of an inverter is greater
to 15 minutes, as compared to an inverter. than that of a UPS. It can provide supplies
Therefore, UPS supplies power for short for hours depending on its capacity. Hence,
duration. inverters supply power for long duration.
Switching time The switching time of a UPS is of the The switching time of an inverter is about
order of 2 to 5 milliseconds. Hence, a UPS 200 m/s to 500 m/s. Thus, the switching of
provides fast switching. inverters is slower than UPS.
Protection UPS provides necessary protection against Inverters do not provide protection against
abnormal conditions like short circuits, abnormal conditions.
overload, etc.
AVR UPS is equipped with an AVR (Automatic Inverter does not include AVR, thus the
Voltage Regulator) that provides a constant output voltage of the inverter may vary due
output voltage to the load. to change in load.
Circuit complexity UPS has relatively more complex circuits. Inverter is a simple circuit than a UPS.
Cost (for same UPS includes complex circuitry and smart Inverters are less expensive than a UPS.
rating) devices to provide necessary protections
which makes it more expensive than an
inverter.
Maintenance UPS are almost maintenance free, except Due to more wiring and the need of
for the battery. distilled water in inverter batteries, the
inverters require relatively more & frequent
maintenance.
Applications The UPS are used to supply electric power The inverters are used to supply power to
to PCs, workstations, small office and home various domestic electric appliances such
office devices like routers, etc. as lamps, fans, coolers, etc.
UPS Block Diagram
A typical UPS block diagram is shown in block diagram in the picture below
Operating Principle:
In the simplest form, UPS is a supply system that offers uninterrupted power to the AC load by converting DC
into AC. UPS differs from an emergency power supply system or a standby generator, as it can protect devices
from power outages by one or more connected batteries. The battery run time is relatively short, typically 5 to 15
minutes, but it is long enough to bring the auxiliary power supply online or protect devices from shutting down.
In normal operating conditions, the current is drawn from the AC main power supply or grid, while UPS provides
load current in case of a power outage. Here the battery is used as the backup source to deliver power to the load
in case of power failure.
92
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 56 - 63