Page 112 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 112
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
2 Output frequency depends on the input frequency.
3 Line interactive UPS has no power factor correction circuit.
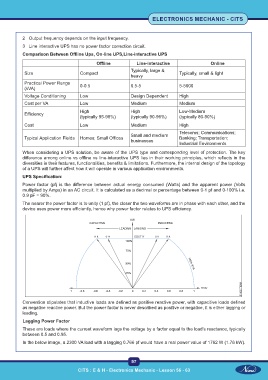
Comparison Between Offline Ups, On-line UPS,Line-interactive UPS
Offline Line-interactive Online
Typically, large &
Size Compact Typically, small & light
heavy
Practical Power Range 0-0.5 0.5-5 5-5000
(kVA)
Voltage Conditioning Low Design Dependent High
Cost per VA Low Medium Medium
High High Low-Medium
Efficiency
(typically 95-98%) (typically 90-96%) (typically 80-90%)
Cost Low Medium High
Telecoms; Communications;
Small and medium
Typical Application Fields Homes; Small Offices Banking; Transportation;
businesses
Industrial Environments
When considering a UPS solution, be aware of the UPS type and corresponding level of protection. The key
difference among online vs offline vs line-interactive UPS lies in their working principles, which reflects in the
diversities in their features, functionalities, benefits & limitations. Furthermore, the internal design of the topology
of a UPS will further affect how it will operate in various application environments.
UPS Specification:
Power factor (pf) is the difference between actual energy consumed (Watts) and the apparent power (Volts
multiplied by Amps) in an AC circuit. It is calculated as a decimal or percentage between 0-1 pf and 0-100% i.e.
0.9 pF = 90%.
The nearer the power factor is to unity (1 pf), the closer the two waveforms are in phase with each other, and the
device uses power more efficiently, hence why power factor relates to UPS efficiency.
Convention stipulates that inductive loads are defined as positive reactive power, with capacitive loads defined
as negative reactive power. But the power factor is never described as positive or negative, it is either lagging or
leading.
Lagging Power Factor
These are loads where the current waveform lags the voltage by a factor equal to the load’s reactance, typically
between 0.5 and 0.95.
In the below image, a 2300 VA load with a lagging 0.766 pf would have a real power value of 1762 W (1.76 kW).
97
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 56 - 63