Page 200 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 200
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
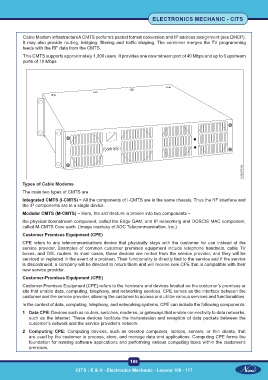
Cable Modem InfrastructureA CMTS performs packet format conversion and IP address assignment (see DHCP).
It may also provide routing, bridging, filtering and traffic shaping. The combiner merges the TV programming
feeds with the RF data from the CMTS.
This CMTS supports approximately 1,300 users. It provides one downstream port of 40 Mbps and up to 6 upstream
ports of 10 Mbps
Types of Cable Modems
The main two types of CMTS are
Integrated CMTS (I-CMTS) − All the components of I-CMTS are in the same chassis. Thus the RF interface and
the IP components are in a single device.
Modular CMTS (M-CMTS) − Here, the architecture is broken into two components −
the physical downstream component, called the Edge QAM, and IP networking and DOSCIS MAC component,
called M-CMTS Core each. (Image courtesy of ADC Telecommunication, Inc.)
Customer Premises Equipment (CPE)
CPE refers to any telecommunications device that physically stays with the customer for use instead of the
service provider. Examples of common customer premises equipment include telephone handsets, cable TV
boxes, and DSL routers. In most cases, these devices are rented from the service provider, and they will be
serviced or replaced in the event of a problem. Their functionality is directly tied to the service and if the service
is discontinued, a company will be directed to return them and will receive new CPE that is compatible with their
new service provider..
Customer-Premises Equipment (CPE)
Customer-Premises Equipment (CPE) refers to the hardware and devices located on the customer’s premises or
site that enable data, computing, telephony, and networking services. CPE serves as the interface between the
customer and the service provider, allowing the customer to access and utilize various services and functionalities.
In the context of data, computing, telephony, and networking systems, CPE can include the following components:
1 Data CPE: Devices such as routers, switches, modems, or gateways that enable connectivity to data networks,
such as the internet. These devices facilitate the transmission and reception of data packets between the
customer’s network and the service provider’s network.
2 Computing CPE: Computing devices, such as desktop computers, laptops, servers, or thin clients, that
are used by the customer to process, store, and manage data and applications. Computing CPE forms the
foundation for running software applications and performing various computing tasks within the customer’s
premises.
185
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 108 - 117