Page 204 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 204
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
When a mobile user A moves from one cell to another cell then BSC 1 signal strength loses for the mobile User
A and the signal strength of BSC 2 increases and thus ongoing calls or data connectivity for mobile users goes
on without interruption.
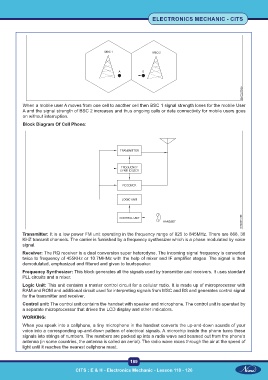
Block Diagram Of Cell Phone:
Transmitter: It is a low power FM unit operating in the frequency range of 825 to 845MHz. There are 666, 30
KHZ transmit channels. The carrier is furnished by a frequency synthesizer which is a phase modulated by voice
signal.
Receiver: The RQ receiver is a dual conversion super heterodyne. The incoming signal frequency is converted
twice to frequency of 455KHz or 10.7MHMz with the help of mixer and IF amplifier stages. The signal is then
demodulated, emphasized and filtered and given to loudspeaker.
Frequency Synthesizer: This block generates all the signals used by transmitter and receivers. It uses standard
PLL circuits and a mixer.
Logic Unit: This unit contains a master control circuit for a cellular radio. It is made up of microprocessor with
RAM and ROM and additional circuit used for interpreting signals from MSC and BS and generates control signal
for the transmitter and receiver.
Control unit: The control unit contains the handset with speaker and microphone. The control unit is operated by
a separate microprocessor that drives the LCD display and other indicators.
WORKING:
When you speak into a cellphone, a tiny microphone in the handset converts the up-and-down sounds of your
voice into a corresponding up-and-down pattern of electrical signals. A microchip inside the phone turns these
signals into strings of numbers. The numbers are packed up into a radio wave and beamed out from the phone’s
antenna (in some countries, the antenna is called an aerial). The radio wave races through the air at the speed of
light until it reaches the nearest cellphone mast.
189
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 118 - 126