Page 89 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 89
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
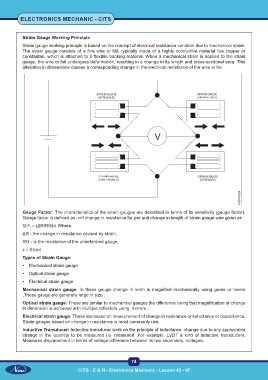
Strain Gauge Working Principle
Strain gauge working principle is based on the concept of electrical resistance variation due to mechanical strain.
The strain gauge consists of a fine wire or foil, typically made of a highly conductive material like copper or
constantan, which is attached to a flexible backing material. When a mechanical strain is applied to the strain
gauge, the wire or foil undergoes deformation, resulting in a change in its length and cross-sectional area. This
alteration in dimensions causes a corresponding change in the electrical resistance of the wire or foil.
Gauge Factor: The characteristics of the strain gauges are described in terms of its sensitivity (gauge factor).
Gauge factor is defined as unit change in resistance for per unit change in length of strain gauge wire given as
G.F. = (ΔR/RG)/ε Where,
ΔR - the change in resistance caused by strain,
RG - is the resistance of the undeformed gauge,
ε – Strain
Types of Strain Gauge:
• Mechanical strain gauge
• Optical strain gauge
• Electrical strain gauge
Mechanical strain gauge: In these gauge change in lenth is magnified mechanically using gears or levers
.These gauge are generally large in size .
Optical strain gauge: These are similar to mechanical gauges the difference being that magnification of change
in dimension is achieved with multiple reflectors using mirrors .
Electrical strain gauge: These are based on measurement of change in resistance or inductance or capacitance.
Strain gauges based on change in resistance is most commonly use.
Inductive Transducer: Inductive transducer work on the principle of inductance change due to any appreciable
change in the quantity to be measured i.e. measured .For example .LVDT a kind of inductive transducers.
Measures displacement in terms of voltage difference between its two secondary voltages.
74
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 43 - 47