Page 32 - CITS - Fitter - Trade Theory
P. 32
FITTER - CITS
4 Grades of files: Files are manufactured in different types and grades to meet the various needs. Files are
specified according to their length, grade, cut and shape. Length is the distance from the tip of a file to the heel.
File grades are determined by the spacing of the teeth.
Rough file:A rough file is used for removing rapidly a larger quantity of metal.
It is mostly used for trimming the rough edges of soft metal castings.
Bastard file:A bastard file is used in cases where there is a heavy reduction of material
Second cut file:A second cut file is used to give a good finish on metals.
It is excellent to file hard metals. It is useful for bringing the jobs close to the finishing size.
Smooth file: A smooth file is used to remove small quantity of material and to give a good finish.
Dead smooth:A dead smooth file is used to bring the material to accurate size with a high degree of finish.
The most used grades of files are bastard, second cut, smooth and dead smooth. These are the the grades
recommended by the bureau of Indian standards (BIS)
Different sizes of files with the same grade will have varying sizes of teeth. In longer files, the teeth will be coarser.
The number of cutting edge in rows in each of the above grades over a Length of 10mm as shown in .
Types of files and its care and maintence
Definition of file: It is made of high carbon steel HCS To make the surface flat by cutting And chipping by saw.
It is used to remove unnecessary .Metal from the job or for finishing. Filing allowance is usually keptfrom0.02mm
to 0-5mm.
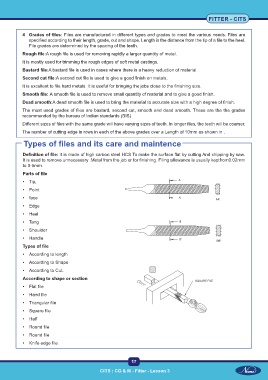
Parts of file
• Tip,
• Point
• face
• Edge
• Heel
• Tang
• Shoulder
• Handle
Types of file
• According to length
• According to Shape
• According to Cut.
According to shape or section
• Flat file
• Hand file
• Triangular file
• Square file
• Half
• Round file
• Round file
• Knife edge file.
17
CITS : CG & M - Fitter - Lesson 3