Page 37 - CITS - Fitter - Trade Theory
P. 37
FITTER - CITS
3 Half-round nose chisel: They are used for cutting curved grooves (oil grooves). A half-round nose chisel is a
specialized type of chisel with a curved cutting edge resembling a half-circle or half-oval shape at the tip.
4 Diamond point chisel: A half-round nose chisel is a specialized type of chisel with a curved cutting edge
resembling a half- circle or half-oval shape at the tip.
5 Web chisel: A web chisel, also known as a “corner chisel,” is a specialized type of chisel designed for cutting
square corners or cleaning out corners in woodworking and carpentry.
Specification
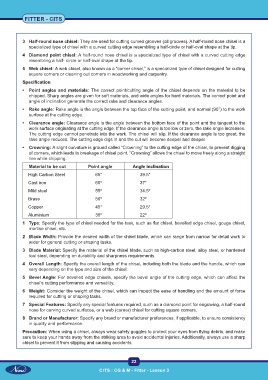
• Point angles and materials: The correct point/cutting angle of the chisel depends on the material to be
chipped. Sharp angles are given for soft materials, and wide angles for hard materials. The correct point and
angle of inclination generate the correct rake and clearance angles.
• Rake angle: Rake angle is the angle between the top face of the cutting point, and normal (90°) to the work
surface at the cutting edge.
• Clearance angle: Clearance angle is the angle between the bottom face of the point and the tangent to the
work surface originating at the cutting edge. If the clearance angle is too low or zero, the rake angle increases.
The cutting edge cannot penetrate into the work. The chisel will slip. If the clearance angle is too great, the
rake angle reduces. The cutting edge digs in and the cut will become deeper and deeper.
• Crowning: A slight curvature is ground called “Crowning” to the cutting edge of the chisel, to prevent digging
of corners, which leads to breakage of chisel point. “Crowning” allows the chisel to move freely along a straight
line while chipping.
Material to be cut Point angle Angle inclination
High Carbon Steel 65° 39.5°
Cast iron 60º 37°
Mild steel 55º 34.5º
Brass 50º 32º
Copper 45° 29.5°
Aluminium 30º 22º
1 Type: Specify the type of chisel needed for the task, such as flat chisel, bevelled edge chisel, gouge chisel,
mortise chisel, etc.
2 Blade Width: Provide the desired width of the chisel blade, which can range from narrow for detail work to
wider for general cutting or shaping tasks.
3 Blade Material: Specify the material of the chisel blade, such as high-carbon steel, alloy steel, or hardened
tool steel, depending on durability and sharpness requirements.
4 Overall Length: Specify the overall length of the chisel, including both the blade and the handle, which can
vary depending on the type and size of the chisel.
5 Bevel Angle: For bevelled edge chisels, specify the bevel angle of the cutting edge, which can affect the
chisel’s cutting performance and versatility.
6 Weight: Consider the weight of the chisel, which can impact the ease of handling and the amount of force
required for cutting or shaping tasks.
7 Special Features: Specify any special features required, such as a diamond point for engraving, a half-round
nose for carving curved surfaces, or a web (corner) chisel for cutting square corners.
8 Brand or Manufacturer: Specify any brand or manufacturer preferences, if applicable, to ensure consistency
in quality and performance.
Precaution: When using a chisel, always wear safety goggles to protect your eyes from flying debris, and make
sure to keep your hands away from the striking area to avoid accidental injuries. Additionally, always use a sharp
chisel to prevent it from slipping and causing accidents.
22
CITS : CG & M - Fitter - Lesson 3