Page 105 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 105
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
• Unburnt Hydrocarbons are oxidized into water/steam.
• Carbon monoxide is oxidized into carbon Dioxide
• Oxides are converted into Nitrogen and Oxygen
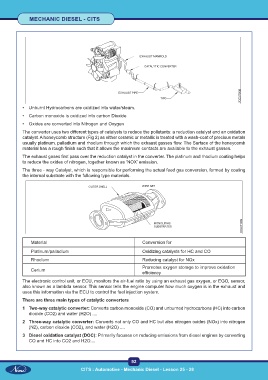
The converter uses two different types of catalysts to reduce the pollutants: a reduction catalyst and an oxidation
catalyst. A honeycomb structure (Fig 2) as either ceramic or metallic is treated with a wash-coat of precious metals
usually platinum, palladium and rhodium through which the exhaust gasses flow. The Surface of the honeycomb
material has a rough finish such that it allows the maximum contacts are available to the exhaust gasses.
The exhaust gases first pass over the reduction catalyst in the converter. The platinum and rhodium coating helps
to reduce the oxides of nitrogen, together known as ‘NOX’ emission.
The three - way Catalyst, which is responsible for performing the actual feed gas conversion, formed by coating
the internal substrate with the following type materials.
Material Conversion for
Platinum/palladium Oxidizing catalysts for HC and CO
Rhodium Reducing catalyst for NOx
Promotes oxygen storage to improve oxidation
Cerium
efficiency
The electronic control unit, or ECU, monitors the air-fuel ratio by using an exhaust gas oxygen, or EGO, sensor,
also known as a lambda sensor. This sensor tells the engine computer how much oxygen is in the exhaust and
uses this information via the ECU to control the fuel injection system.
There are three main types of catalytic converters
1 Two-way catalytic converter: Converts carbon monoxide (CO) and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon
dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) ....
2 Three-way catalytic converter: Converts not only CO and HC but also nitrogen oxides (NOx) into nitrogen
(N2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O) ....
3 Diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC): Primarily focuses on reducing emissions from diesel engines by converting
CO and HC into CO2 and H2O....
92
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 25 - 28