Page 297 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 297
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
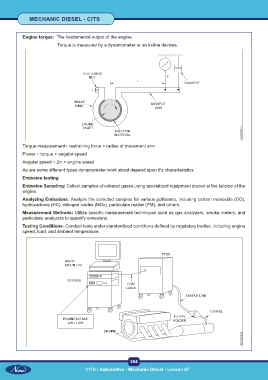
Engine torque: The fundamental output of the engine.
Torque is measured by a dynamometer or an in-line devices.
Torque measurement= restraining force × radius of movement arm
Power = torque × angular speed
Angular speed = 2π × engine speed
As are some different types dynamometer work about depend upon it’s characteristics
Emission testing
Emission Sampling: Collect samples of exhaust gases using specialized equipment placed at the tailpipe of the
engine.
Analyzing Emissions: Analyze the collected samples for various pollutants, including carbon monoxide (CO),
hydrocarbons (HC), nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and others.
Measurement Methods: Utilize specific measurement techniques such as gas analyzers, smoke meters, and
particulate analyzers to quantify emissions.
Testing Conditions: Conduct tests under standardized conditions defined by regulatory bodies, including engine
speed, load, and ambient temperature.
284
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 87