Page 327 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 327
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
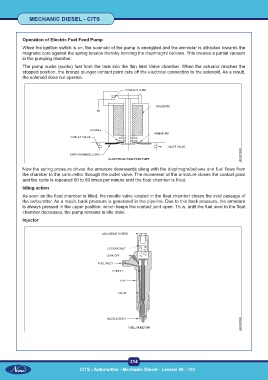
Operation of Electric Fuel Feed Pump
When the ignition switch is on, the solenoid of the pump is energized and the ammeter is attracted towards the
magnetic core against the spring tension thereby bending the diaphragm/ bellows. This creates a partial vacuum
in the pumping chamber.
The pump sucks (sucks) fuel from the tank into the thin Inlet Valve chamber. When the actuator reaches the
stopped position, the bronze plunger contact point cuts off the electrical connection to the solenoid. As a result,
the solenoid does not operate.
Now the spring pressure drives the armature downwards along with the diaphragm/bellows and fuel flows from
the chamber to the carburettor through the outlet valve. The movement of the armature closes the contact point
and the cycle is repeated 50 to 60 times per minute until the float chamber is filled.
Idling action
As soon as the float chamber is filled, the needle valve located in the float chamber closes the inlet passage of
the carburettor. As a result, back pressure is generated in the pipeline. Due to this back pressure, the armature
is always pressed in the upper position, which keeps the contact joint open. Thus, until the fuel level in the float
chamber decreases, the pump remains in idle state.
Injector
314
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 98 - 103