Page 331 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 331
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
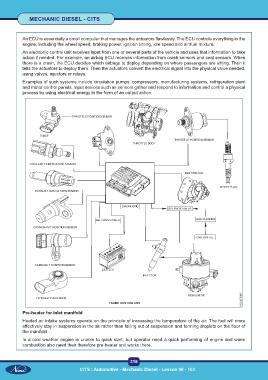
An ECU is essentially a small computer that manages the actuators flawlessly. The ECU controls everything in the
engine, including the wheel speed, braking power, ignition timing, idle speed and air/fuel mixture.
An electronic control unit receives input from one or several parts of the vehicle and uses that information to take
action if needed. For example, an airbag ECU receives information from crash sensors and seat sensors. When
there is a crash, the ECU decides which airbags to deploy depending on where passengers are sitting. Then it
tells the actuators to deploy them. Then the actuators convert the electrical signal into the physical value needed,
using valves, injectors or relays.
Examples of such systems include circulation pumps, compressors, manufacturing systems, refrigeration plant
and motor control panels. Input devices such as sensors gather and respond to information and control a physical
process by using electrical energy in the form of an output action.
Pre-heater for inlet manifold
Heated air intake systems operate on the principle of increasing the temperature of the air. The fuel will more
effectively stay in suspension in the air rather than falling out of suspension and forming droplets on the floor of
the manifold.
In a cold weather engine is unable to quick start, but operator need a quick performing of engine and warm
combustion also need their therefore pre-heater unit works there.
318
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 98 - 103