Page 58 - CITS - WCS - Mechanical
P. 58
WORKSHOP SCIENCE - CITS
Thermal expansion is used in various applications such as railroad track buckling, engine coolants, mercury in
thermometers, joint expansion, etc. This article will cover the thermal expansion of solids, liquids, and gasses and
their applications.
∆L = αL∆T is the formula for linear thermal expansion, where ΔL is the change in length L, ΔT is the change in
temperature, and is the linear expansion coefficient, which varies slightly with temperature
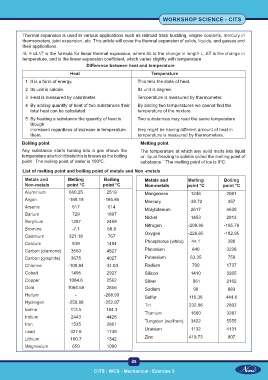
Difference between heat and temperature
Heat Temperature
1 It is a form of energy. This tells the state of heat.
2 Its unit is calorie. Its unit is degree.
3 Heat is measured by calorimeter. Temperature is measured by thermometer.
4 By adding quantity of heat of two substances their By adding two temperatures we cannot find the
total heat can be calculated. temperature of the mixture.
5 By heating a substance the quantity of heat is Two substances may read the same temperature
though
increased regardless of increase in temperature. they might be having different amount of heat in
them. temperature is measured by thermometers.
Boiling point Melting point
Any substance starts turning into a gas shows the The temperature at which any solid melts into liquid
temperature at which it boils this is known as the boiling or liquid freezing to solid is called the melting point of
point. The boiling point of water is 100 C. substance. ` The melting point of ice is 0 C.
0
0
List of melting point and boiling point of metals and Non -metals
Metals and Melting Boiling Metals and Melting Boiling
Non-metals point °C point °C Non-metals point °C point °C
Aluminium 660.25 2519 Manganese 1246 2061
Argon -189.19 -185.85 Mercury -38.72 357
Arsenic 817 614 Molybdenum 2617 4639
Barium 729 1897 Nickel 1453 2913
Beryllium 1287 2469
Bromine -7.1 58.8 Nitrogen -209.86 -195.79
Cadmium 321.18 767 Oxygen -226.65 -182.95
Calcium 839 1484 Phosphorus (white) 44.1 280
Carbon (diamond) 3550 4827 Plutonium 640 3228
Carbon (graphite) 3675 4027 Potassium 63.35 759
Chlorine -100.84 -34.04 Radium 700 1737
Cobalt 1495 2927 Silicon 1410 3265
Copper 1084.6 2562 Silver 961 2162
Gold 1064.58 2856 Sodium 98 883
Helium - -268.93 Sulfur 115.36 444.6
Hydrogen -259.98 -252.87 Tin 232.06 2602
Iodine 113.5 184.3 Titanium 1660 3287
Iridium 2443 4428
Iron 1535 2861 Tungsten (wolfram) 3422 5555
Lead 327.6 1749 Uranium 1132 4131
Lithium 180.7 1342 Zinc 419.73 907
Magnesium 650 1090
45
CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 3 CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 3