Page 74 - CITS - WCS - Mechanical
P. 74
WORKSHOP SCIENCE - CITS
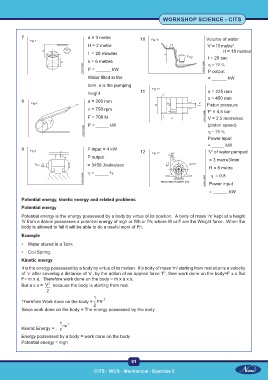
7 d = 3 metre 10 Volume of water
H = 2 metre ‘V’ = 10 metre
3
t = 20 minutes H = 18 metres
t = 20 sec
s = 6 metres
η = 70 %
P = ______ kW P output
Water filled in the = ______ kW
tank. s is the pumping
height 11 d = 225 mm
s = 450 mm
8 d = 200 mm
Piston pressure
n = 750 rpm
‘P’ = 4.5 bar
F = 700 N V = 2.5 metre/sec
P = _____ kW (piston speed)
η = 70 %
Power input
= _____ kW
9 P input = 4 kW
12 ‘V’ of water pumped
P output
= 3 metre3/min
= 3450 Joules/sec
H = 6 metre
η = ______ %
η = 0.8
Power input
= ______ kW
Potential energy, kinetic energy and related problems
Potential energy
Potential energy is the energy possessed by a body by virtue of its position. A body of mass ‘m’ kept at a height
‘h’ from a datum possesses a potential energy of mgh or Wh or Fh; where W or F are the Weight force. When the
body is allowed to fall it will be able to do a useful work of Fh.
Example
• Water stored in a Tank
• Coil Spring.
Kinetic energy
It is the energy possessed by a body by virtue of its motion. If a body of mass ‘m’ starting from rest attains a velocity
of ‘v’ after covering a distance of ‘s’, by the action of an applied force ‘F’, then work done on the body=F x s But
F= m x a. Therefore work done on the body = m x a x s.
2
But a x s = V because the body is starting from rest.
2
1
Therefore Work done on the body = . mv 2
2
Since work done on the body = The energy possessed by the body
1 2
mv
Kinetic Energy = . 2
Energy possessed by a body = work done on the body
Potential energy = mgh
61
CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 5 CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 5