Page 75 - CITS - WCS - Mechanical
P. 75
WORKSHOP SCIENCE - CITS
Kinetic energy = mv 2
If friction is neglected potential energy = Kinetic energy
Example
• Rolling vehicle
• Rotating fly wheel
• Flowing water
• Falling weight
Potential energy
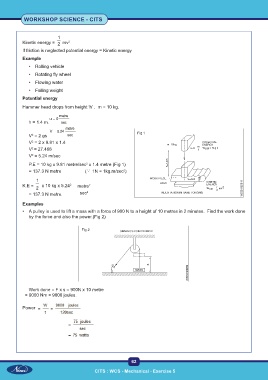
Hammer head drops from height ‘h’ . m = 10 kg.
metre
u = 0
h = 1.4 m. sec
V = 5.24 metre
V = 2 gs sec
2
V = 2 x 9.81 x 1.4
2
V = 27.468
2
V = 5.24 m/sec
2
P.E = 10 kg x 9.81 metre/sec x 1.4 metre (Fig 1)
2
= 137.3 N metre ( 1N = 1kg.m/sec )
2
1 2
mv
K.E = x 10 kg x 5.24 metre 2
2
2
= 137.3 N metre. sec 2
Examples
• A pulley is used to lift a mass with a force of 900 N to a height of 10 metres in 2 minutes. Find the work done
by the force and also the power.(Fig 2)
Fig 2
Work done = F x s = 900N x 10 metre
= 9000 Nm = 9000 joules.
Power
62
CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 5