Page 80 - CITS - WCS - Mechanical
P. 80
WORKSHOP SCIENCE - CITS
Angle of friction
Angle made by the resultant of normal reaction and limiting friction
with the normal reaction is called the angle of friction. The coefficient of
static friction is equal to the tangent of the angle of friction.
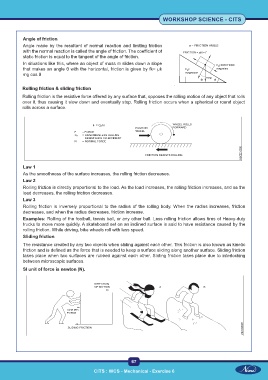
In situations like this, where an object of mass m slides down a slope
that makes an angle θ with the horizontal, friction is given by fk= µk
mg cos θ
Rolling friction & sliding friction
Rolling friction is the resistive force offered by any surface that, opposes the rolling motion of any object that rolls
over it, thus causing it slow down and eventually stop. Rolling friction occurs when a spherical or round object
rolls across a surface.
Law 1
As the smoothness of the surface increases, the rolling friction decreases.
Law 2
Rolling friction is directly proportional to the load. As the load increases, the rolling friction increases, and as the
load decreases, the rolling friction decreases.
Law 3
Rolling friction is inversely proportional to the radius of the rolling body. When the radius increases, friction
decreases, and when the radius decreases, friction increase.
Examples: Rolling of the football, tennis ball, or any other ball. Less rolling friction allows tires of Heavy-duty
trucks to move more quickly. A skateboard set on an inclined surface is said to have resistance caused by the
rolling friction. While driving, bike wheels roll with less speed.
Sliding friction
The resistance created by any two objects when sliding against each other. This friction is also known as kinetic
friction and is defined as the force that is needed to keep a surface sliding along another surface. Sliding friction
takes place when two surfaces are rubbed against each other. Sliding friction takes place due to interlocking
between microscopic surfaces.
SI unit of force is newton (N).
67
CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 6 CITS : WCS - Mechanical - Exercise 6