Page 136 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 136
WELDER - CITS
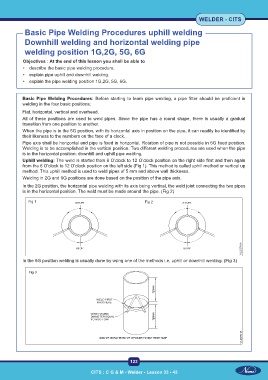
Basic Pipe Welding Procedures uphill welding
Downhill welding and horizontal welding pipe
welding position 1G,2G, 5G, 6G
Objectives : At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• describe the basic pipe welding procedure.
• explain pipe uphill and downhill welding.
• explain the pipe welding position 1G,2G, 5G, 6G.
Basic Pipe Welding Procedures: Before starting to learn pipe welding, a pipe fitter should be proficient in
welding in the four basic positions:
Flat, horizontal, vertical and overhead.
All of these positions are used to weld pipes. Since the pipe has a round shape, there is usually a gradual
transition from one position to another.
When the pipe is in the 5G position, with its horizontal axis in position on the pipe, it can readily be identified by
their likeness to the numbers on the face of a clock.
Pipe axis shall be horizontal and pipe is fixed in horizontal. Rotation of pipe is not possible in 5G fixed position.
Welding is to be accomplished in the vertical position. Two different welding procedures are used when the pipe
is in the horizontal position: downhill and uphill pipe welding.
Uphill welding: The weld is started from 6 O’clock to 12 O’clock position on the right side first and then again
from the 6 O’clock to 12 O’clock position on the left side (Fig 1). This method is called uphill method or vertical up
method. This uphill method is used to weld pipes of 5 mm and above wall thickness.
Welding in 2G and 6G positions are done based on the position of the pipe axis.
In the 2G position, the horizontal pipe welding with its axis being vertical, the weld joint connecting the two pipes
is in the horizontal position. The weld must be made around the pipe. (Fig 2)
Fig 1 Fig 2
In the 6G position welding is usually done by using one of the methods i.e. uphill or downhill welding. (Fig 3)
Fig 3
123
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 33 - 43