Page 56 - CITS - Welder - Trade Theory
P. 56
WELDER - CITS
Weld slope and weld rotation in respect of all the four positions are shown above.
Definitions of welding positions with respect to their slope and rotation angles a Table is given below.
Definition of welding position
Position Symbol Slope Rotation
Flat or down hand F Not exceeding 10° Not exceeding 10°
Horizontal H Not exceeding10° Exceeding 10° but not beyond 90°
Vertical V Exceeding 45° Any.
Overhead O Not exceeding 45°. Exceeding 90°
Polarity : Types and Application
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• state of polarity in arc welding
• describe the types of polarity
• describe the application of straight and reverse polarity
Introduction: Polarity in welding refers to the direction of current flow between the welding electrode and work
piece. It plays a critical role in determining the characteristics of the welding arc & resulting weld.
Definition of polarity
Direction of current flow called as polarity.
Types of Polarity
Polarity is categorized into two types.
1 Straight polarity (DCEN)(DCSP)
2 Reverse polarity (DCEP)(DCRP)
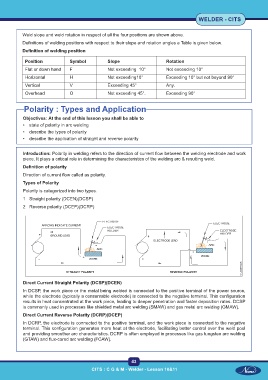
Direct Current Straight Polarity (DCSP)(DCEN)
In DCSP, the work piece or the metal being welded is connected to the positive terminal of the power source,
while the electrode (typically a consumable electrode) is connected to the negative terminal. This configuration
results in heat concentrated at the work piece, leading to deeper penetration and faster deposition rates. DCSP
is commonly used in processes like shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) and gas metal arc welding (GMAW).
Direct Current Reverse Polarity (DCRP)(DCEP)
In DCRP, the electrode is connected to the positive terminal, and the work piece is connected to the negative
terminal. This configuration generates more heat at the electrode, facilitating better control over the weld pool
and providing smoother arc characteristics. DCRP is often employed in processes like gas tungsten arc welding
(GTAW) and flux-cored arc welding (FCAW).
43
CITS : C G & M - Welder - Lesson 10&11