Page 314 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 314
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Power factor meter
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to:
• explain the construction and connection of 3-phase dynamometer type power factor meter
• explain the construction, connection and operation of a 3-phase moving iron type power factor meter
• explain the construction, connection and operation of a single phase moving iron type power factor meter.
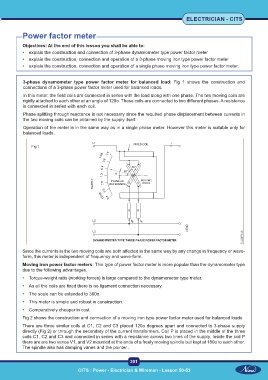
3-phase dynamometer type power factor meter for balanced load: Fig 1 shows the construction and
connections of a 3-phase power factor meter used for balanced loads.
In this meter, the field coils are connected in series with the load along with one phase. The two moving coils are
rigidly attached to each other at an angle of 120o. These coils are connected to two different phases. A resistance
is connected in series with each coil.
Phase splitting through reactance is not necessary since the required phase displacement between currents in
the two moving coils can be obtained by the supply itself.
Operation of the meter is in the same way as in a single phase meter. However this meter is suitable only for
balanced loads.
Fig 1
Since the currents in the two moving coils are both affected in the same way by any change in frequency or wave-
form, this meter is independent of frequency and wave-form.
Moving iron power factor meters: This type of power factor meter is more popular than the dynamometer type
due to the following advantages.
• Torque-weight ratio (working forces) is large compared to the dynamometer type meter.
• As all the coils are fixed there is no ligament connection necessary.
• The scale can be extended to 360o.
• This meter is simple and robust in construction.
• Comparatively cheaper in cost.
Fig 2 shows the construction and connection of a moving iron type power factor meter used for balanced loads.
There are three similar coils at C1, C2 and C3 placed 120o degrees apart and connected to 3-phase supply
directly (Fig 2) or through the secondary of the current transformers. Coil P is placed in the middle of the three
coils C1, C2 and C3 and connected in series with a resistance across two lines of the supply. Inside the coil P
there are are two vanes V1, and V2 mounted at the ends of a freely moving spindle but kept at 180o to each other.
The spindle also has damping vanes and the pointer .
301
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 50-53 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 50-53