Page 315 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 315
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
The rotating magnetic field produced by the three coils C C and C interacts with the flux produced by the coil
1,
3
2
P. This causes the moving system to take up an angular position depending upon the phase angle of the current.
Single phase moving iron power factor meter: A single phase moving iron power factor meter (Fig 3) uses a
phase splitting network comprising of a capacitor, an inductor and a resistor.
3-phase power factor meters for unbalanced load: For measurement of power factor in 3-phase unbalanced
systems 2-element or 3-element power factor meters with each element with a current coil and pressure coil is
used. The pressure coils are (moving coils) similar to that of single phase P.F. meters are mounted one below the
other on a single spindle. The pointer shows the resultant power factor.
Fig 2 & 3
Measurement of 3 phase power by single and two wattmeters
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to:
• explain the measurement 3 phase power using single wattmeter
• explain the measurement of 3 phase power using two wattmeters
• calculate the power factor by two wattmeter method power measurement.
The measurement of power: The number of wattmeters used to obtain power in a three-phase system depends
on whether the load is balanced or not, and whether the neutral point, if there is one, is accessible
- Measurement of power in a star-connected balanced load with neutral point is possible by a single wattmeter
- Measurement of power in a star or delta-connected, balanced or unbalanced load (with or without neutral) is
possible with two wattmeter method
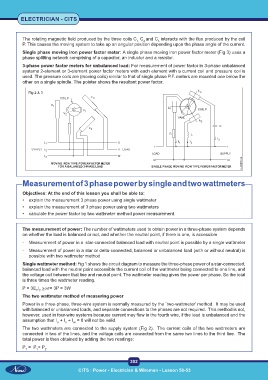
Single wattmeter method: Fig 1 shows the circuit diagram to measure the three-phase power of a star-connected,
balanced load with the neutral point accessible the current coil of the wattmeter being connected to one line, and
the voltage coil between that line and neutral point. The wattmeter reading gives the power per phase. So the total
is three times the wattmeter reading.
P = 3E I cos= 3P = 3W
P P
The two wattmeter method of measuring power
Power in a three-phase, three-wire system is normally measured by the `two-wattmeter’ method. It may be used
with balanced or unbalanced loads, and separate connections to the phases are not required. This method is not,
however, used in four-wire systems because current may flow in the fourth wire, if the load is unbalanced and the
assumption that I + I + I = 0 will not be valid.
V
W
U
The two wattmeters are connected to the supply system (Fig 2). The current coils of the two wattmeters are
connected in two of the lines, and the voltage coils are connected from the same two lines to the third line. The
total power is then obtained by adding the two readings:
P = P + P .
T 1 2
302
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 50-53