Page 316 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 316
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
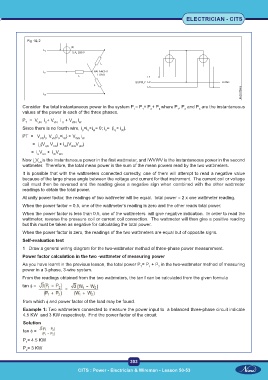
Fig 1& 2
Consider the total instantaneous power in the system P = P + P + P where P , P and P are the instantaneous
2
3
T
1
3
2
1
values of the power in each of the three phases.
P = V i + V i + V I
T UN U VN V WN W
Since there is no fourth wire, i +i +i = 0; i = (i + i ).
W
V
U
V
W
U
PT = V i V (i +i ) + V i
UN U
W
WN W
VN U
= i (V V ) + i (V V )
U
UN
WN
UN
VN
W
= i V + i V
U UV W WV
Now i V is the instantaneous power in the first wattmeter, and iWVWV is the instantaneous power in the second
U
UV
wattmeter. Therefore, the total mean power is the sum of the mean powers read by the two wattmeters.
It is possible that with the wattmeters connected correctly, one of them will attempt to read a negative value
because of the large phase angle between the voltage and current for that instrument. The current coil or voltage
coil must then be reversed and the reading given a negative sign when combined with the other wattmeter
readings to obtain the total power.
At unity power factor, the readings of two wattmeter will be equal. total power = 2 x one wattmeter reading.
When the power factor = 0.5, one of the wattmeter’s reading is zero and the other reads total power.
When the power factor is less than 0.5, one of the wattmeters will give negative indication. In order to read the
wattmeter, reverse the pressure coil or current coil connection. The wattmeter will then give a positive reading
but this must be taken as negative for calculating the total power.
When the power factor is zero, the readings of the two wattmeters are equal but of opposite signs.
Self-evaluation test
1 Draw a general wiring diagram for the two-wattmeter method of three-phase power measurement.
Power factor calculation in the two -wattmeter of measuring power
As you have learnt in the previous lesson, the total power P = P + P in the two-wattmeter method of measuring
T
1
2
power in a 3-phase, 3-wire system.
From the readings obtained from the two wattmeters, the tan f can be calculated from the given formula
tan f =
from which f and power factor of the load may be found.
Example 1: Two wattmeters connected to measure the power input to a balanced three-phase circuit indicate
4.5 KW and 3 KW respectively. Find the power factor of the circuit.
Solution
tan f =
P = 4.5 KW
1
P = 3 KW
2
303
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 50-53 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 50-53