Page 33 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 33
ELECTRICIAN - CITS ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Drills and drilling machines
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to:
• state the functions of drills
• name the parts of a drill
• name the drill bit holders
• state the uses of countersunking bits.
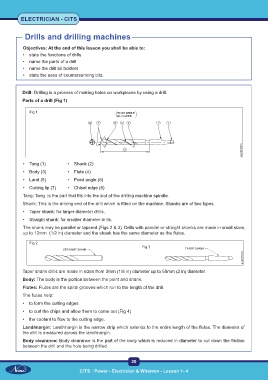
Drill: Drilling is a process of making holes on workpieces by using a drill.
Parts of a drill (Fig 1)
Fig 1
• Tang (1) • Shank (2)
• Body (3) • Flute (4)
• Land (5) • Point angle (6)
• Cutting lip (7) • Chisel edge (8)
Tang: Tang is the part that fits into the slot of the drilling machine spindle.
Shank: This is the driving end of the drill which is fitted on the machine. Shanks are of two types.
• Taper shank: for larger diameter drills.
• Straight shank: for smaller diameter drills.
The shank may be parallel or tapered.(Figs 2 & 3) Drills with parallel or straight shanks are made in small sizes,
up to 12mm (1/2 in) diameter and the shank has the same diameter as the flutes.
Fig 2
Fig 3
Taper shank drills are made in sizes from 3mm (1/8 in) diameter up to 50mm (2 in) diameter.
Body: The body is the portion between the point and shank.
Flutes: Flutes are the spiral grooves which run to the length of the drill.
The flutes help:
• to form the cutting edges
• to curl the chips and allow them to come out (Fig 4)
• the coolant to flow to the cutting edge.
Land/margin: Land/margin is the narrow strip which extends to the entire length of the flutes. The diameter of
the drill is measured across the land/margin.
Body clearance: Body clearance is the part of the body which is reduced in diameter to cut down the friction
between the drill and the hole being drilled.
20 21
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 1- 4