Page 38 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 38
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
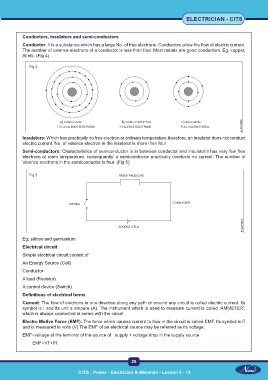
Conductors, insulators and semi-conductors
Conductor: It is a substance which has a large No. of free electrons. Conductors allow the flow of electric current.
The number of valence electrons of a conductor is less than four. Most metals are good conductors. Eg; copper,
Al etc. (Fig 4)
Fig 4
Insulators: Which has practically no free electron at ordinary temperature.therefore, an insulator does not conduct
electric current. No. of valence electron in the insulator is more than four.
Semi-conductors: Characteristics of semiconductor is in between conductor and insulator.it has very few free
electrons at room temperature. consequently’ a semiconductor practically conducts no current. The number of
Valence electrons in the semiconductor is four. (Fig 5)
Fig 5
Eg; silicon and germanium
Electrical circuit
Simple electrical circuit consist of
An Energy Source (Cell)
Conductor
A load (Resistor)
A control device (Switch)
Definitions of electrical terms
Current: The flow of electrons in one direction along any path or around any circuit is called electric current. Its
symbol is I and its unit s ampere (A). The instrument which is used to measure current is called ‘AMMETER’,
which is always connected in series with the circuit.
Electro Motive Force (EMF): The force which causes current to flow in the circuit is called EMF. Its symbol is E
and is measured in volts (V) The EMF of an electrical source may be referred as its voltage.
EMF=voltage at the terminal of the source of supply + voltage drop in the supply source
EMF=VT+IR
25
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 5 - 12