Page 41 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 41
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
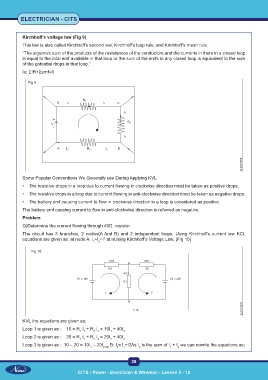
Kirchhoff’s voltage law (Fig 9)
This law is also called Kirchhoff’s second law, Kirchhoff’s loop rule, and Kirchhoff’s mesh rule.
“The algebraic sum of the products of the resistances of the conductors and the currents in them in a closed loop
is equal to the total emf available in that loop or the sum of the emfs in any closed loop is equivalent to the sum
of the potential drops in that loop.”
Ie; ΣIR+Σemf=0
Fig 9
Some Popular Conventions We Generally use During Applying KVL
• The resistive drops in a loop due to current flowing in clockwise direction must be taken as positive drops.
• The resistive drops in a loop due to current flowing in anti-clockwise direction must be taken as negative drops.
• The battery emf causing current to flow in clockwise direction in a loop is considered as positive.
The battery emf causing current to flow in anti-clockwise direction is referred as negative.
Problem
Q)Determine the current flowing through 40Ω resistor.
The circuit has 3 branches, 2 nodes(A And B) and 2 independent loops. Using Kirchhoff’s current law KCL
equations are given as: at node A: I +I =I at nUsing Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law, (Fig 10)
3
2
1
Fig 10
KVL the equations are given as;
Loop 1 is given as : 10 = R I + R I = 10I + 40I 3
1
3 3
1 1
Loop 2 is given as : 20 = R I + R I = 20I + 40I
2 2 3 3 2 3
Loop 3 is given as : 10 – 20 = 10I – 20I 2ode B: I = I +I2As I is the sum of I + I we can rewrite the equations as;
3
2
1
1
1
3
28
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 5 - 12