Page 46 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 46
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Application of parallel circuit
An electrical system in which one section can fail and other sections continue to operates as parallel circuits. The
electric system used in homes consist of many parallel circuits.
An automobile electrical system uses parallel circuit for lights, horn, radio etc.
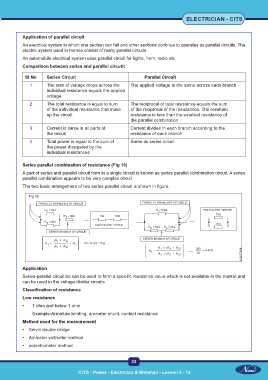
Comparison between series and parallel circutit
Sl No Series Circuit Parallel Circuit
1 The sum of voltage drops across the The applied voltage is the same across each branch
individual resistance equals the applied
voltage
2 The total resistance is equal to sum The reciprocal of total resistance equals the sum
of the individual resistance that make of the reciprocal of the resistances. The resultant
up the circuit resistance is less than the smallest resistance of
the parallel combination
3 Current is same in all parts of Current divides in each branch according to the
the circuit resistance of each branch
4 Total power is equal to the sum of Same as series circuit.
the power dissipated by the
individual resistances
Series parallel combination of resistance (Fig 19)
A part of series and parallel circuit form in a single circuit is known as series parallel combination circuit. A series
parallel combination appears to be very complex circuit
The two basic arrangement of two series parallel circuit is shown in figure.
Fig 19
Application
Series-parallel circuit be can be used to form a specific resistance value which is not available in the market and
can be used in the voltage divider circuits
Classification of resistance
Low resistance
• 1 ohm and below 1 ohm
Example-Armature winding, ammeter shunt, contact resistance
Method used for the measurement
• Kelvin double bridge
• Ammeter voltmeter method
• potentiometer method
33
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 5 - 12