Page 50 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 50
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Copper: It has Reddish colour. It has best conductivity next to silver. It has Largest current density compared to
other metals. Hence the volume required to carry a given current is less for given length. It can be drawn in to thin
wires(malleable) and sheets(ductile). It has a high resistance to atmospheric corrosion; hence it can serve for a
long time. It can be joined without any special provision to prevent electrolytic action. It is durable and has high
scrap value. Next to copper aluminum is the metal used for electrical conductors.
Aluminium: It has Whitish colour. When compared to copper conductivity is 60.6 percent. hence for same current
capacity, the cross-section for the aluminum wire should be larger than that for the copper wire. It is Lighter in
weight. It is Malleable and ductile. But losses its tensile strength on reduction of the cross-sectional area. It is
cheaper than copper.
Measurement of wire size: While selecting the cable size, the electrician has to take in to consideration the
proposed connected load, future changes in load’ the length of the cable run and the permissible voltage drop in
the cable. To measure the size of conductors we use normally a standard wire gauge or a micro meter for more
accurate result.
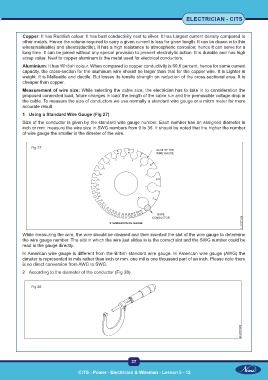
1 Using a Standard Wire Gauge (Fig 27)
Size of the conductor is given by the standard wire gauge number. Each number has an assigned diameter in
inch or mm. measure the wire size in SWG numbers from 0 to 36. It should be noted that the higher the number
of wire gauge the smaller is the dimeter of the wire.
Fig 27
While measuring the wire, the wire should be cleaned and then inserted the slot of the wire gauge to determine
the wire gauge number. The slot in which the wire just slides in is the correct slot and the SWG number could be
read in the gauge directly.
In American wire gauge is different from the British standard wire gauge. In American wire gauge (AWG) the
dimeter is represented in mils rather than inch or mm. one mil is one thousand part of an inch. Please note there
is no direct conversion from AWG to SWG.
2 According to the diameter of the conductor (Fig 28)
Fig 28
37
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 5 - 12