Page 43 - Electrician - TT (Volume 1)
P. 43
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
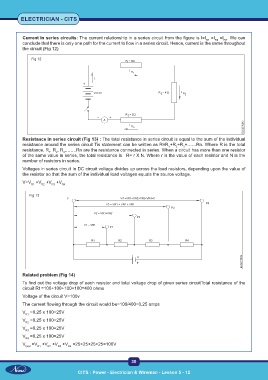
Current in series circuits: The current relationship in a series circuit from the figure is I=I =I =I . We can
R2
R1
R3
conclude that there is only one path for the current to flow in a series circuit. Hence, current is the same throughout
the circuit (Fig 12)
Fig 12
Resistance in series circuit (Fig 13) : The total resistance in series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual
resistance around the series circuit Tis statement can be written as R=R +R +R +……Rn. Where R is the total
1
2
3
resistance, R , R , R ,…….Rn are the resistance connected in series. When a circuit has more than one resistor
1
2
3
of the same value in series, the total resistance is R= r X N. Where r is the value of each resistor and N is the
number of resistors in series.
Voltages in series circuit In DC circuit voltage divides up across the load resistors, depending upon the value of
the resistor so that the sum of the individual load voltages equals the source voltage.
V=V +V +V +V R4
R1
R2
R3
Fig 13
Related problem (Fig 14)
To find out the voltage drop of each resistor and total voltage drop of given series circuitTotal resistance of the
circuit Rt =100+100+100+100=400 ohms
Voltage of the circuit V=100v
The current flowing through the circuit would be=100/400=0,25 amps
V =0.25 x 100=25V
R1
V =0.25 x 100=25V
R2
V =0.25 x 100=25V
R3
V =0.25 x 100=25V
R4
V total =V +V +V +V =25+25+25+25=100V
R2
R3
R4
R1
30
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 5 - 12