Page 128 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 128
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
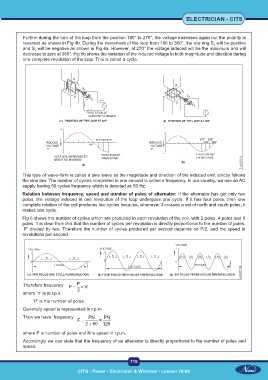
Further during the turn of the loop from the position 180° to 270°, the voltage increases again but the polarity is
reversed as shown in Fig 4b. During the movement of the loop from 180 to 360°, the slip ring S will be positive
2
and S will be negative as shown in Fig 4a. However, at 270° the voltage induced will be the maximum and will
1
decrease to zero at 360°. Fig 5b shows the variation of the induced voltage in both magnitude and direction during
one complete revolution of the loop. This is called a cycle.
This type of wave-form is called a sine wave as the magnitude and direction of the induced emf, strictly follows
the sine law. The number of cycles completed in one second is called a frequency. In our country, we use an AC
supply having 50 cycles frequency which is denoted as 50 Hz.
Relation between frequency, speed and number of poles of alternator: If the alternator has got only two
poles, the voltage induced in one revolution of the loop undergoes one cycle. If it has four poles, then one
complete rotation of the coil produces two cycles because, whenever it crosses a set of north and south poles, it
makes one cycle.
Fig 6 shows the number of cycles which are produced in each revolution of the coil, with 2 poles, 4 poles and 6
poles. It is clear from this that the number of cycles per revolution is directly proportional to the number of poles,
`P’ divided by two. Therefore the number of cycles produced per second depends on P/2, and the speed in
revolutions per second.
Therefore frequency F P ''
n
where `n’ is in r.p.s. 2
`P’ is the number of poles.
Generally speed is represented in r.p.m.
Then we have frequency PN PN
F =
2 60 120
where P is number of poles and N is speed in r.p.m.
Accordingly we can state that the frequency of an alternator is directly proportional to the number of poles and
speed.
115
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 76-85