Page 162 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 162
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Fig 9 Fig 10
Testing of armature winding
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to:
• describe the methods of testing armature, such as the
– winding resistance test
– insulation resistance test
– growler test
– voltage drop test..
Testing the winding : After an armature is wound and the leads are connected to the commutator, a test should
be conducted. From this test, defects may be revealed, which might have occurred during winding. The common
defects in armature windings are grounding, shorts in the coils, open in the coil and reversal in the coil connection.
These defects can be located by different test procedures.
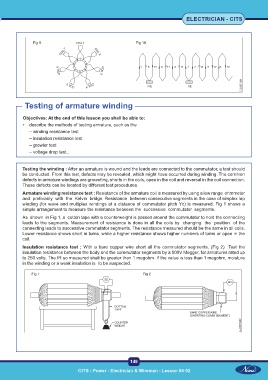
Armature winding resistance test : Resistance of the armature coil is measured by using a low range ohmmeter
and preferably with the Kelvin bridge. Resistance between consecutive segments in the case of simplex lap
winding (for wave and multiplex windings at a distance of commutator pitch Yc) is measured. Fig 1 shows a
simple arrangement to measure the resistance between the successive commutator segments.
As shown in Fig 1, a cotton tape with a counterweight is passed around the commutator to hold the connecting
leads to the segments. Measurement of resistance is done in all the coils by changing the position of the
connecting leads to successive commutator segments. The resistance measured should be the same in all coils.
Lower resistance shows short in turns, while a higher resistance shows higher numbers of turns or open in the
coil.
Insulation resistance test : With a bare copper wire short all the commutator segments. (Fig 2) Test the
insulation resistance between the body and the commutator segments by a 500V Megger, for armatures rated up
to 250 volts. The IR so measured shall be greater than 1 megohm. If the value is less than 1 megohm, moisture
in the winding or a weak insulation is to be suspected.
Fig 1 Fig 2
148 149
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 86-92