Page 167 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 167
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
STEP NO.3
Determine the required cross-sectional area of the core of the transformer.
For finding the cross-sectional area, certain parameters like the flux density of the metal used for laminations,
frequency of supply, allowable current density in the winding wire and power input to the transformer need to be
known.
Cross section = 20 x 21=420 sq.mm or 4.2 sq. cm
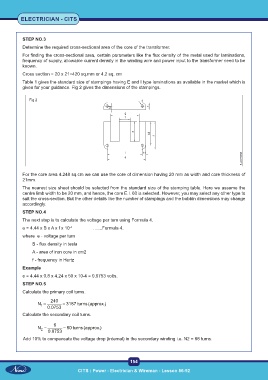
Table 1 gives the standard size of stampings having E and I type laminations as available in the market which is
given for your guidance. Fig 2 gives the dimensions of the stampings.
Fig 2
For the core area 4.248 sq.cm we can use the core of dimension having 20 mm as width and core thickness of
21mm.
The nearest size sheet should be selected from the standard size of the stamping table. Here we assume the
centre limb width to be 20 mm, and hence, the core E.I. 60 is selected. However, you may select any other type to
suit the cross-section. But the other details like the number of stampings and the bobbin dimensions may change
accordingly.
STEP NO.4
The next step is to calculate the voltage per turn using Formula 4.
e = 4.44 x B x A x f x 10 .......Formula 4.
-4
where e - voltage per turn
B - flux density in tesla
A - area of iron core in cm2
f - frequency in Hertz
Example
e = 4.44 x 0.8 x 4.24 x 50 x 10-4 = 0.0753 volts.
STEP NO.5
Calculate the primary coil turns.
240
N 1 0.0753 3187 turns (approx.)
Calculate the secondary coil turns.
6
N 2 0.0753 80 turns (approx.)
Add 10% to compensate the voltage drop (internal) in the secondary winding i.e. N2 = 88 turns.
154 155
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 86-92