Page 168 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 168
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
STEP NO.6
Calculate the size of wire with respect to the input power.
P = E x I ; I = P/E and according to the example,
Primary current = I = 15/240 = 0.0625A
1
Secondary current = I = 15/6 = 2.5A.
2
Cross-section of primary conductor considering 3A/mm2 as current density will be
A = 0.0625/3 = 0.020833 mm2
Diameter = 0.1628 mm
Say i.e. = 0.160 mm dia. or 37 SWG approximately
Cross-section of secondary conductor considering 3A/mm2 as current density will be
A = 2.5/3A = 0.8333 mm2
Diameter = 1.029 mm
Say = 1.00 mm dia. Hence 19 SWG.
STEP NO.7
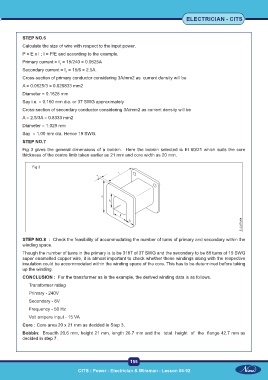
Fig 3 gives the general dimensions of a bobbin. Here the bobbin selected is EI 60/21 which suits the core
thickness of the centre limb taken earlier as 21 mm and core width as 20 mm.
Fig 3
STEP NO.8 : Check the feasibility of accommodating the number of turns of primary and secondary within the
winding space.
Though the number of turns in the primary is to be 3187 of 37 SWG and the secondary to be 88 turns of 19 SWG
super enamelled copper wire, it is atmost important to check whether these windings along with the respective
insulation could be accommodated within the winding space of the core. This has to be determined before taking
up the winding.
CONCLUSION : For the transformer as in the example, the derived winding data is as follows.
Transformer rating
Primary - 240V
Secondary - 6V
Frequency - 50 Hz
Volt ampere input - 15 VA
Core : Core area 20 x 21 mm as decided in Step 3.
Bobbin: Breadth 20.6 mm, height 21 mm, length 26.7 mm and the total height of the flange 42.7 mm as
decided in step 7.
154 155
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 86-92