Page 194 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 194
ELECTRICIAN - CITS ELECTRICIAN - CITS
Single phase, split phase type motor winding
(Concentric coil winding)
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to:
• state the important points to be followed while winding split phase motors
• explain about coil distribution in concentric winding
• prepare the winding table, draw the connection and developed diagrams for concentric coil winding in single
phase, split phase type motors.
Split phase type: In general, single phase motors use a capacitor to split the phase. Some motors are, as found
in fans, have the capacitor permanently connected to the supply. In some motors, the capacitor is used only
for the starting period, then while running it is disconnected from the supply by the use of a centrifugal switch
mechanism. In some other types of motors there are two capacitors, one for starting and the other for running.
However, depending upon the power, function and the design of the motor, the capacitor value will be different in
each case. Observe this point every time you come across the split phase motor.
There are certain points to be followed while winding a split phase motor.
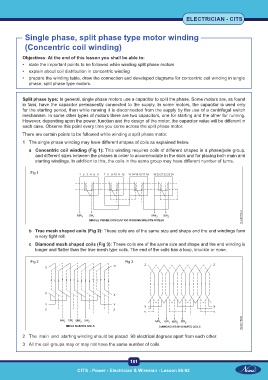
1 The single phase winding may have different shapes of coils as explained below.
a Concentric coil winding (Fig 1): This winding requires coils of different shapes in a phase/pole group,
and different sizes between the phases in order to accommodate in the slots and for placing both main and
starting windings. In addition to this, the coils in the same group may have different number of turns.
Fig 1
b True mesh shaped coils (Fig 2): These coils are of the same size and shape and the end windings form
a very tight roll.
c Diamond mesh shaped coils (Fig 3): These coils are of the same size and shape and the end winding is
longer and flatter than the true mesh type coils. The end of the coils has a loop, knuckle or nose.
Fig 2 Fig 3
2 The main and starting winding should be placed 90 electrical degrees apart from each other.
3 All the coil groups may or may not have the same number of coils.
180 181
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 86-92 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 86-92