Page 332 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 332
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
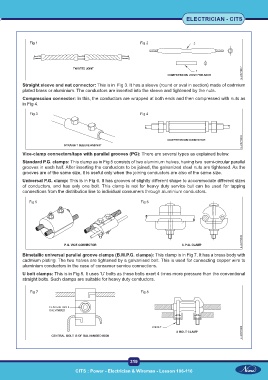
Fig 1 Fig 2
Straight sleeve and nut connector: This is in Fig 3. It has a sleeve (round or oval in section) made of cadmium
plated brass or aluminium. The conductors are inserted into the sleeve and tightened by the nuts.
Compression connector: In this, the conductors are wrapped at both ends and then compressed with nuts as
in Fig 4.
Fig 3 Fig 4
Vice-clamp connectors/taps with parallel grooves (PG): There are several types as explained below.
Standard P.G. clamps: This clamp as in Fig 5 consists of two aluminium halves, having two semi-circular parallel
grooves in each half. After inserting the conductors to be joined, the galvanized steel nuts are tightened. As the
grooves are of the same size, it is useful only when the joining conductors are also of the same size.
Universal P.G. clamp: This is in Fig 6. It has grooves of slightly different shape to accommodate different sizes
of conductors, and has only one bolt. This clamp is not for heavy duty service but can be used for tapping
connections from the distribution line to individual consumers through aluminium conductors.
Fig 5 Fig 6
Bimetallic universal parallel groove clamps (B.M.P.G. clamps): This clamp is in Fig 7. It has a brass body with
cadmium plating. The two halves are tightened by a galvanised bolt. This is used for connecting copper wire to
aluminium conductors in the case of consumer service connections.
U bolt clamps: This is in Fig 8. It uses ‘U’ bolts as these bolts exert 4 times more pressure than the conventional
straight bolts. Such clamps are suitable for heavy duty conductors.
Fig 7 Fig 8
319
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 106-116 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 106-116