Page 355 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 355
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
In rainy season there is no issue regards to driving your EV. Plus even in the worst case there are many protective
layers to a car and battery will remain safe and separate itself if at all water come in.
Working of Public charging Stations
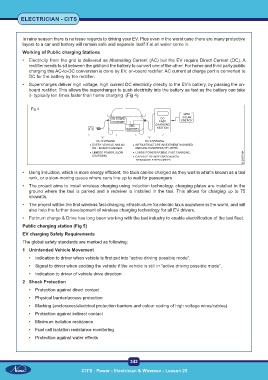
• Electricity from the grid is delivered as Alternating Current (AC) but the EV require Direct Current (DC). A
rectifier needs to sit between the grid and the battery to convert one of the other. For home and third party public
charging this AC-to-DC conversion is done by EV, on-board rectifier. AC current at charge port is converted to
DC for the battery by the rectifier.
• Supercharges deliver high voltage, high current DC electricity directly to the EV’s battery, by passing the on-
board rectifier. This allows the supercharger to push electricity into the battery as fast as the battery can take
it- typically ten times faster than home charging. (Fig 4)
Fig 4
• Using induction, which is more energy efficient, the taxis can be charged as they wait in what’s known as a taxi
rank, or a slow-moving queue where cans line up to wait for passengers.
• The project aims to install wireless charging using induction technology. charging plates are installed in the
ground where the taxi is parked and a receiver is installed in the taxi. This allows for charging up to 75
kilowatts.
• The project will be the first wireless fast-charging infrastructure for electric taxis anywhere in the world, and will
also help the further development of wireless charging technology for all EV drivers.
• Fortnum charge & Drive has long been working with the taxi industry to enable electrification of the taxi fleet.
Public charging station (Fig 5)
EV charging Safety Requirements
The global safety standards are marked as following:
1 Unintended Vehicle Movement
• Indication to driver when vehicle is first put into “active driving possible mode”.
• Signal to driver when exciting the vehicle if the vehicle is still in “active driving possible mode”.
• Indication to driver of vehicle drive direction
2 Shock Protection
• Protection against direct contact
• Physical barrier/access protection
• Marking (enclosures/electrical protection barriers and colour coding of high voltage wires/cables)
• Protection against indirect contact
• Minimum isolation resistance
• Fuel cell isolation resistance monitoring
• Protection against water effects
342
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 25