Page 350 - Electrician - TT (Volume 2)
P. 350
ELECTRICIAN - CITS
• DC Level 1: Supplies a maximum of 80 kW at 50–1000 V.
• DC Level 2: Supplies a maximum of 400 kW at 50–1000 V.
Additional standards released by SAE for charging include SAE J3068 (three-phase AC charging, using the Type
2 connector defined in IEC 62196-2) and SAE J3105 (automated connection of DC charging devices).
IEC
In 2003, the International Electro technical Commission (IEC) adopted a mwwajority of the SAE J1772 standard
under IEC 62196-1 for international implementation.
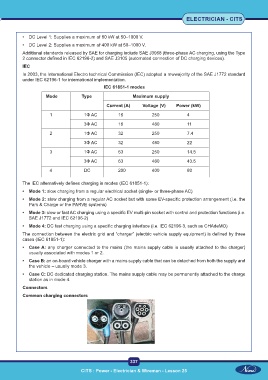
IEC 61851-1 modes
Mode Type Maximum supply
Current (A) Voltage (V) Power (kW)
1 1Φ AC 16 250 4
3Φ AC 16 480 11
2 1Φ AC 32 250 7.4
3Φ AC 32 480 22
3 1Φ AC 63 250 14.5
3Φ AC 63 480 43.5
4 DC 200 400 80
The IEC alternatively defines charging in modes (IEC 61851-1):
• Mode 1: slow charging from a regular electrical socket (single- or three-phase AC)
• Mode 2: slow charging from a regular AC socket but with some EV-specific protection arrangement (i.e. the
Park & Charge or the PARVE systems)
• Mode 3: slow or fast AC charging using a specific EV multi-pin socket with control and protection functions (i.e.
SAE J1772 and IEC 62196-2)
• Mode 4: DC fast charging using a specific charging interface (i.e. IEC 62196-3, such as CHAdeMO)
The connection between the electric grid and “charger” (electric vehicle supply equipment) is defined by three
cases (IEC 61851-1):
• Case A: any charger connected to the mains (the mains supply cable is usually attached to the charger)
usually associated with modes 1 or 2.
• Case B: an on-board vehicle charger with a mains supply cable that can be detached from both the supply and
the vehicle – usually mode 3.
• Case C: DC dedicated charging station. The mains supply cable may be permanently attached to the charge
station as in mode 4.
Connectors
Common charging connectors
337
CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 25 CITS : Power - Electrician & Wireman - Lesson 25