Page 152 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 152
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
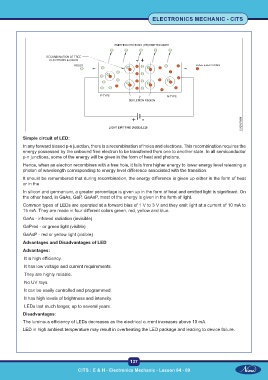
Simple circuit of LED:
In any forward biased p-n junction, there is a recombination of holes and electrons. This recombination requires the
energy possessed by the unbound free electron to be transferred from one to another state. In all semiconductor
p-n junctions, some of the energy will be given in the form of heat and photons.
Hence, when an electron recombines with a free hole, it falls from higher energy to lower energy level releasing a
photon of wavelength corresponding to energy level difference associated with the transition.
It should be remembered that during recombination, the energy difference is given up either in the form of heat
or in the
In silicon and germanium, a greater percentage is given up in the form of heat and emitted light is significant. On
the other hand, in GaAs, GaP, GaAsP, most of the energy is given in the form of light.
Common types of LEDs are operated at a forward bias of 1 V to 3 V and they emit light at a current of 10 mA to
15 mA. They are made in four different colors green, red, yellow and blue.
GaAs - infrared radiation (invisible)
GaPred - or green light (visible)
GaAsP - red or yellow light (visible)
Advantages and Disadvantages of LED
Advantages:
It is high efficiency.
It has low voltage and current requirements.
They are highly reliable.
No UV rays.
It can be easily controlled and programmed.
It has high levels of brightness and intensity.
LEDs last much longer, up to several years.
Disadvantages:
The luminous efficiency of LEDs decreases as the electrical current increases above 10 mA.
LED in high ambient temperature may result in overheating the LED package and leading to device failure.
137
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 84 - 89