Page 155 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 155
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
The photodiode chip comes with two transparent layers.
i SiO, passivation/insulation.
ii Light transmissive polyamide.
The LED is firmly attached to the photodiode with a transparent connecting layer. Standard dies attach process
is used to make all placements.
Advantages of Stacked LEDS:
Some advantages are discussed below.
High Integration:
The stacked LED technology greatly enhances packaging capabilities and flexibility by utilizing conventional IC
assembly equipment. An emitter detector chip set can be inserted into any required integrated package.
Reduce Process Steps:
The method requires fewer process steps and hence, is a more efficient manufacturing method.
Small and Thin Profile Package:
The total package height solely depends on the thickness of the combination of the IC, LED, the very thin polymide,
and the band wire height to the LED.
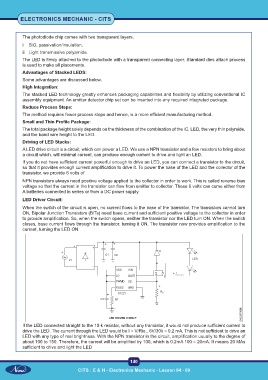
Driving of LED Stacks:
A LED drive circuit is a circuit, which can power a LED. We use a NPN transistor and a few resistors to bring about
a circuit which, will minimal current, can produce enough current to drive and light an LED.
If you do not have sufficient current powerful enough to drive an LED, you can connect a transistor to the circuit,
so that it provides enough current amplification to drive it. To power the base of the LED and the collector of the
transistor, we provide 6 volts of
NPN transistors always need positive voltage applied to the collector in order to work. This is called reverse bias
voltage so that the current in the transistor can flow from emitter to collector. These 6 volts can come either from
A batteries connected in series or from a DC power supply.
LED Driver Circuit:
When the switch of the circuit is open, no current flows to the base of the transistor. The transistors cannot turn
ON, Bipolar Junction Transistors (BITs) need base current and sufficient positive voltage to the collector in order
to provide amplification. So, when the switch opens, neither the transistor nor the LED turn ON. When the switch
closes, base current flows through the transistor, turning it ON. The transistor now provides amplification to the
current, turning the LED ON
If the LED connected straight to the 10-k resistor, without any transistor, it would not produce sufficient current to
drive the LED. The current through the LED would be I = V/Rie., 6V/30k = 0.2 mA. This is not sufficient to drive an
LED with any type of real brightness. With the NPN transistor in the circuit, amplification usually to the degree of
about 100 to 150. Therefore, the current will be amplified by 100, which is 0.2mA 100 = 20mA. It means 20 MAs
sufficient to drive and light the LED
140
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 84 - 89