Page 156 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 156
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
INTRODUCTION
LED Panel Lights have revolutionized the lighting industry with their energy efficiency, durability, and versatility.
They are widely used in various applications, including offices, schools, hospitals, retail stores, and residential
spaces. These panels offer a cost-effective and eco-friendly lighting solution that can significantly reduce energy
consumption while providing high-quality illumination.
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode. They are a special type of diode that convert electrical energy into light. They
have very similar electrical characteristics to a normal PN junction diode. That’s why the symbol of LED is similar
to the normal PN junction diode except that it contains arrows pointing away from the diode indicating that light is
being emitted by the diode.
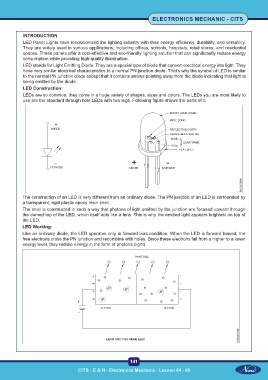
LED Construction:
LEDs are so common, they come in a huge variety of shapes, sizes and colors. The LEDs you are most likely to
use are the standard through hole LEDs with two legs. Following figure shows the parts of it.
The construction of an LED is very different from an ordinary diode. The PN junction of an LED is surrounded by
a transparent, rigid plastic epoxy resin shell.
The shell is constructed in such a way that photons of light emitted by the junction are focused upward through
the domed top of the LED, which itself acts like a lens. This is why the emitted light appears brightest on top of
the LED.
LED Working:
Like an ordinary diode, the LED operates only in forward bias condition. When the LED is forward biased, the
free electrons cross the PN junction and recombine with holes. Since these electrons fall from a higher to a lower
energy level, they radiate energy in the form of photons (light).
141
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 84 - 89