Page 173 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 173
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
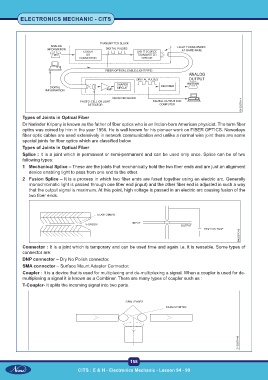
Types of Joints in Optical Fiber
Dr Narinder Kripany is known as the father of fiber optics who is an Indian-born American physicist. The term fiber
optics was coined by him in the year 1956. He is well known for his pioneer work on FIBER OPTICS. Nowadays
fiber optic cables are used extensively in network communication and unlike a normal wire joint there are some
special joints for fiber optics which are classified below
Types of Joints in Optical Fiber
Splice : It is a joint which is permanent or semi-permanent and can be used only once. Splice can be of two
following types:
1 Mechanical Splice – These are the joints that mechanically hold the two fiber ends and are just an alignment
device enabling light to pass from one end to the other.
2 Fusion Splice – It is a process in which two fiber ends are fused together using an electric arc. Generally
monochromatic light is passed through one fiber end (input) and the other fiber end is adjusted in such a way
that the output signal is maximum. At this point, high voltage is passed in an electric arc causing fusion of the
two fiber ends.
Connector : It is a joint which is temporary and can be used time and again i.e. it is reusable. Some types of
connector are:
DNP connector – Dry No Polish connector.
SMA connector – Surface Mount Adapter Connector.
Coupler : It is a device that is used for multiplexing and de-multiplexing a signal. When a coupler is used for de-
multiplexing a signal it is known as a Combiner. There are many types of coupler such as :
T-Coupler- It splits the incoming signal into two parts.
158
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 94 - 99