Page 38 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 38
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
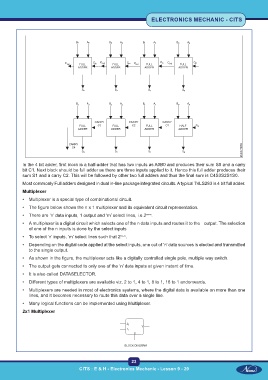
In the 4 bit adder, first block is a half-adder that has two inputs as A0B0 and produces their sum S0 and a carry
bit C1. Next block should be full adder as there are three inputs applied to it. Hence this full adder produces their
sum S1 and a carry C2. This will be followed by other two full adders and thus the final sum is C4S3S2S1S0.
Most commonly Full adders designed in dual in-line package integrated circuits. A typical 74LS283 is 4 bit full adder.
Multiplexer
• Multiplexer is a special type of combinational circuit.
• The figure below shows the n x 1 multiplexer and its equivalent circuit representation.
• There are ‘n’ data inputs, 1 output and ‘m’ select lines, i.e.2 m=n .
• A multiplexer is a digital circuit which selects one of the n data inputs and routes it to the output. The selection
of one of the n inputs is done by the select inputs
• To select ‘n’ inputs, ‘m’ select lines such that 2 m=n .
• Depending on the digital code applied at the select inputs, one out of ‘n’ data sources is elected and transmitted
to the single output.
• As shown in the figure, the multiplexer acts like a digitally controlled single pole, multiple way switch.
• The output gets connected to only one of the ‘n’ data inputs at given instant of time.
• It is also called DATASELECTOR.
• Different types of multiplexers are available viz. 2 to 1, 4 to 1, 8 to 1, 16 to 1 andonwards.
• Multiplexers are needed in most of electronics systems, where the digital data is available on more than one
lines, and it becomes necessary to route this data over a single line.
• Many logical functions can be implemented using Multiplexer.
2x1 Multiplexer
23
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 9 - 29