Page 63 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 63
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computerprocessor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single
integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. It is a programmable device that takes in input, performs some
arithmetic and logical operations over it and produces the desired output. In simple words, a Microprocessor is
a digital device on a chip that can fetch instructions from memory, decode and execute them and give results.
Basics of Microprocessor
A Microprocessor takes a bunch of instructions in machine language and executes them, telling the processor
what it must do. Microprocessor performs three basic things while executing the instruction:
It performs some basic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and some logical operations using
its Arithmetic and Logical Unit (ALU). New Microprocessors also perform operations on floating-point numbers also.
Data in microprocessors can move from one location to another.
It has a Program Counter (PC) register that stores the address of the next instruction based on the value of the
PC, Microprocessor jumps from one location to another and takes decisions.
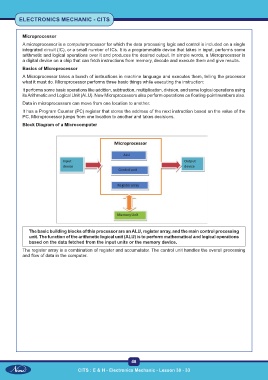
Block Diagram of a Microcomputer
The basic building blocks of this processor are an ALU, register array, and the main control processing
unit. The function of the arithmetic logical unit (ALU) is to perform mathematical and logical operations
based on the data fetched from the input units or the memory device.
The register array is a combination of register and accumulator. The control unit handles the overall processing
and flow of data in the computer.
48
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 30 - 33