Page 66 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 66
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
256 Bytes – Internal RAM where the first RAM with 128 Bytes from 00H to 7FH is once more separated into four
banks through 8 registers in every bank, addressable registers -16 bit & general-purpose registers – 80.
The remaining 128 bytes of the RAM from 80H to FFH include Special Function Registers (SFRs). These registers
control various peripherals such as Serial Port, Timers, all I/O Ports, etc.
Interrupts like External-2 & Internal-3
Oscillator & CLK Circuit.
Control Registers like PCON, SCON, TMOD, TCON, IE, and IP.
16-bit Timers or Counters -2 like T0 & T1.
Program Counter – 16 bit & DPRT (Data Pointer).
I/O Pins – 32 which are arranged like four ports such as P0, P1, P2 & P3.
Stack Pointer (SP) – 8bit & PSW (Processor Status Word).
Serial Data Tx & Rx for Full-Duplex Operation.
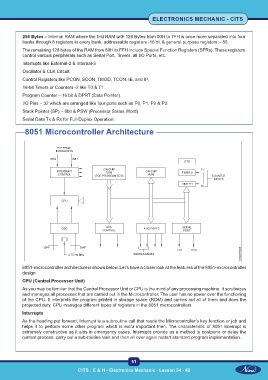
8051 Microcontroller Architecture
8051-microcontroller architecture is shown below. Let’s have a closer look at the features of the 8051-microcontroller
design
CPU (Central Processor Unit)
As you may be familiar that the Central Processor Unit or CPU is the mind of any processing machine. It scrutinizes
and manages all processes that are carried out in the Microcontroller. The user has no power over the functioning
of the CPU. It interprets the program printed in storage space (ROM) and carries out all of them and does the
projected duty. CPU manages different types of registers in the 8051 microcontrollers.
Interrupts
As the heading put forward, Interrupt is a subroutine call that reads the Microcontroller’s key function or job and
helps it to perform some other program which is extra important then. The characteristic of 8051 Interrupt is
extremely constructive as it aids in emergency cases. Interrupts provide us a method to postpone or delay the
current process, carry out a sub-routine task and then all over again restart standard program implementation.
51
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 34 - 42