Page 76 - CITS - Electronic Mechanic - TT - 2024
P. 76
ELECTRONICS MECHANIC - CITS
Pin’s Current limitations
When configured as outputs (logic zero (0)), single port pins can receive a current of 10mA. If all 8 bits of a port
are active, the total current must be limited to 15mA (port P0: 26mA). If all ports (32 bits) are active, total maximum
current must be limited to 71mA. When these pins are configured as inputs (logic 1), built-in pull-up resistors
provide very weak current, but strong enough to activate up to 4 TTL inputs of LS series.
In Short: As seen from description of some ports, even though all of them have similar architecture, it is necessary
to pay attention to which of them is to be used for what and how. For example, if they shall be used as outputs
with high voltage level (5V), then P0 should be avoided because its pins do not have pull-up resistors, thus giving
low logic level only. When using other ports, one should bear in mind that pull-up resistors have a relatively high
resistance, so that their pins can give a current of several hundred Microampere only.
Different Variants of 8051 and their Resources
Features of 8051 made it extremely popular in the market. Because of its popularity and high demand Intel
allowed other manufacturers to fabricate and market different variants of 8051 with a condition that all these
variants should be code compatible with 8051.
This resulted in a lot of variants of 8051 in market, among which 8052 and 8031 are the most popular ones.
Therefore, 8052 and 8031 are considered as the family members of 8051.
8052 – 8052 is the super set of 8051 as it has all the features of 8051 with an extra timer and an extra RAM of 128
bytes. Therefore, 8052 has a total of 256 bytes of RAM and 3 timers in all. Also, all the programs written for 8051
will run on 8052 as 8052 is super set of 8051, but it’s reverse is not true.
8031 – 8031 is referred to as ROM-less microcontroller chip because it has 0 K byes of on-chip ROM. For its
operation, 8031 requires external ROM which aids it in fetch and execute operations. Apart from this, it shares
almost all the features of 8051.
80C31/80C52: The 80C31 and 80C52 are enhanced versions of the 8031 and 8052, respectively. They have
additional features such as an on-chip oscillator, an expanded interrupt structure, and a power-down mode. These
microcontrollers are also compatible with the 8051 in terms of pinout and instruction set.
AT89C51/52: The AT89C51 and AT89C52 are popular derivatives of the 8051 developed by Atmel Corporation.
They have additional features such as an on-chip flash memory, an expanded interrupt structure, and a power-
down mode. These microcontrollers are also compatible with the 8051 in terms of pinout and instruction set,
making it easy to migrate code between them.
STC89C5x: The STC89C5x series of microcontrollers are based on the 8051 architectures but have additional
features such as an on-chip flash memory, an expanded interrupt structure, and a power-down mode. They also
have higher clock speeds and more I/O pins than the 8051. However, they are not fully compatible with the 8051
in terms of pinout and instruction set, so code migration between them requires some modifications.
P89V51RD2: The P89V51RD2 is a derivative of the 8051 developed by NXP Semiconductors. It has additional
features such as an on-chip flash memory, an expanded interrupt structure, and a power-down mode. It also has
a dual-data pointer and a programmable counter array. Like the STC89C5x, it is not fully compatible with the 8051
in terms of pinout and instruction set.
Comparison of 8051 with its other family members
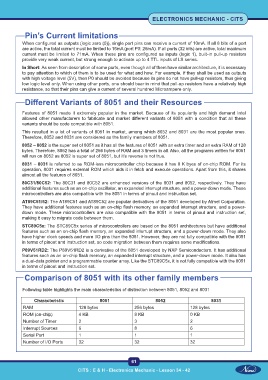
Following table highlights the main characteristics of distinction between 8051, 8052 and 8031
Characteristic 8051 8052 8031
RAM 128 bytes 256 bytes 128 bytes
ROM (on-chip) 4 KB 8 KB 0 KB
Number of Timer 2 3 2
Interrupt Sources 6 8 6
Serial Port 1 1 1
Number of I/O Ports 32 32 32
61
CITS : E & H - Electronics Mechanic - Lesson 34 - 42