Page 116 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 116
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
Fuel pump: The function of fuel pump is to pump petrol and feed to carburetor. These pump can supply petrol
in sufficient quality at all type temperature and make proper a pressure on petrol line. So that to avoid locking of
vapors on heating of petrol called mechanical air lock. Generally, there or two types of pumps used in vehicles.
a Mechanical fuel pump
b Electrical fuel pump
Mechanical fuel pump
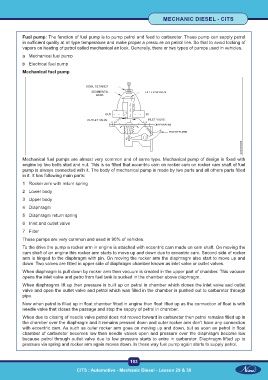
Mechanical fuel pumps are almost very common and of same type. Mechanical pump of design is fixed with
engine by two bolts stud and nut. This is so fitted that eccentric cam on rocker cam on rocker cam shaft of fuel
pump is always connected with it. The body of mechanical pump is made by two parts and all others parts fitted
in it. It has following main parts:
1 Rocker arm with return spring
2 Lower body
3 Upper body
4 Diaphragm
5 Diaphragm return spring
6 Inlet and outlet valve
7 Filter
These pumps are very common and used in 90% of vehicles.
To the drive the pump a rocker arm in engine is attached with eccentric cam made on cam shaft. On moving the
cam shaft of an engine this rocker arm starts to move up and down due to eccentric cam. Second side of rocker
arm is hinged to the diaphragm with pin. On moving the rocker arm the diaphragm also start to move up and
down. Two valves are fitted in upper side of diaphragm chamber known as inlet valve or outlet valves.
When diaphragm is pull down by rocker arm then vacuum is created in the upper part of chamber. This vacuum
opens the inlet valve and petro from fuel tank is sucked in the chamber above diaphragm.
When diaphragms lift up then pressure is built up on petrol in chamber which closes the inlet valve and outlet
valve and open the outlet valve and petrol which was filled in the chamber is pushed out to carburetor through
pipe.
Now when petrol is filled up in float chamber fitted in engine then float lifted up as the connection of float is with
needle valve that closes the passage and stop the supply of petrol in chamber.
When due to closing of needle valve petrol does not moved forward in carburetor then petrol remains filled up in
the chamber over the diaphragm and it remains pressed down and outer rocker arm don’t have any connection
with eccentric cam. As such as outer rocker arm goes on moving up and down, but as soon as petrol in float
chamber of carburetor becomes low then needle valves open and pressure over the diaphragm become low
because petrol through outlet valve due to low pressure starts to entre in carburetor. Diaphragm lifted up to
pressure via spring and rocker arm again moves down. In these way fuel pump again starts to supply petrol.
103
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 29 & 30 CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 29 & 30