Page 353 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 353
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
Main control systems in diesel engine
• It controls the fuel for idling.
• It controls the fuel for high speed.
• It controls the fuel according to the speed and load conditions.
• It controls the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve.
Working
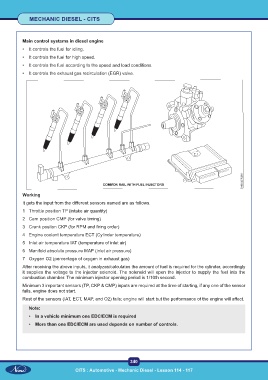
It gets the input from the different sensors named are as follows.
1 Throttle position TP (intake air quantity)
2 Cam position CMP (for valve timing)
3 Crank positon CKP (for RPM and firing order)
4 Engine coolant temperature ECT (Cylinder temperature)
5 Inlet air temperature IAT (temperature of inlet air)
6 Manifold absolute pressure MAP (inlet air pressure)
7 Oxygen O2 (percentage of oxygen in exhaust gas)
After receiving the above inputs, it analyzes/calculates the amount of fuel is required for the cylinder, accordingly
it supplies the voltage to the injector solenoid. The solenoid will open the injector to supply the fuel into the
combustion chamber. The minimum injector opening period is 1/10th second.
Minimum 3 important sensors (TP, CKP & CMP) inputs are required at the time of starting, if any one of the sensor
fails, engine does not start.
Rest of the sensors (IAT, ECT, MAP, and O2) fails; engine will start but the performance of the engine will affect.
Note:
• In a vehicle minimum one EDC/ECM is required
• More than one EDC/ECM are used depends on number of controls.
340
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 114 - 117