Page 354 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 354
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
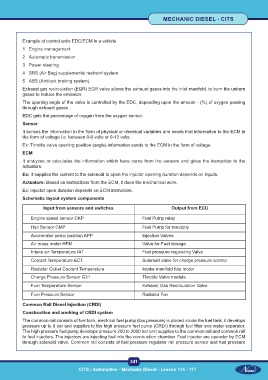
Example of control units EDC/ECM in a vehicle
1 Engine management
2 Automatic transmission
3 Power steering
4 SRS (Air Bag) supplemental restraint system
5 ABS (Antilock braking system)
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) EGR valve allows the exhaust gases into the inlet manifold, to burn the unburn
gases to reduce the emission.
The opening angle of the valve is controlled by the EDC, depending upon the amount - (%) of oxygen passing
through exhaust gases.
EDC gets the percentage of oxygen from the oxygen sensor.
Sensor
It senses the information in the form of physical or chemical variables and sends that information to the ECM in
the form of voltage i.e. between 0-6 volts or 0-12 volts.
Ex: Throttle valve opening position (angle) information sends to the ECM in the form of voltage.
ECM
It analyzes or calculates the information which have come from the sensors and gives the instruction to the
actuators.
Ex: It supplies the current to the solenoid to open the injector opening duration depends on Inputs.
Actuators: Based on instructions from the ECM, it does the mechanical work.
Ex: Injector open duration depends on ECM instruction.
Schematic layout system components
Input from sensors and switches Output from ECU
Engine speed sensor CKP Fuel Pump relay
Hall Sensor CMP Fuel Pump for resupply
Accelerator pedal position APP Injection Valves
Air mass meter HFM Valve for Fuel dosage
Intake air Temperature IAT Fuel pressure regulating Valve
Coolant Temperature ECT Solenoid valve for charge pressure control
Radiator Outlet Coolant Temperature Intake manifold flap motor
Charge Pressure Sensor G31 Throttle Valve module
Fuel Temperature Sensor Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve
Fuel Pressure Sensor Radiator Fan
Common Rail Diesel Injection (CRDI)
Construction and working of CRDI system
The common rail consists of fuel tank, electrical fuel pump (low pressure) is placed inside the fuel tank, it develops
pressure up to 6 bar and supplies to the high pressure fuel pump (CRDI) through fuel filter and water separator.
The high pressure fuel pump develops pressure 200 to 2000 bar and supplies to the common rail and common rail
to fuel injectors. The injectors are injecting fuel into the combustion chamber. Fuel injector are operator by ECM
through solenoid valve. Common rail consists of fuel pressure regulator rail pressure sensor and fuel pressure
341
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 114 - 117