Page 73 - Mechanic Diesel - TT
P. 73
MECHANIC DIESEL - CITS
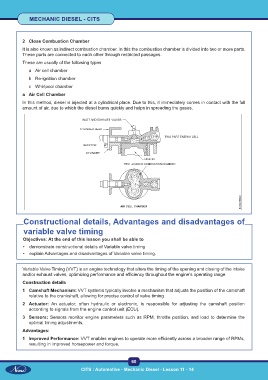
2 Close Combustion Chamber
It is also known as indirect combustion chamber. In this the combustion chamber is divided into two or more parts.
These parts are connected to each other through restricted passages.
These are usually of the following types
a Air cell chamber
b Re-ignition chamber
c Whirlpool chamber
a Air Cell Chamber
In this method, diesel is injected at a cylindrical place. Due to this, it immediately comes in contact with the full
amount of air, due to which the diesel burns quickly and helps in spreading the gases.
Constructional details, Advantages and disadvantages of
variable valve timing
Objectives: At the end of this lesson you shall be able to
• demonstrate constructional details of Variable valve timing
• explain Advantages and disadvantages of Variable valve timing.
Variable Valve Timing (VVT) is an engine technology that alters the timing of the opening and closing of the intake
and/or exhaust valves, optimizing performance and efficiency throughout the engine’s operating range.
Construction details
1 Camshaft Mechanism: VVT systems typically involve a mechanism that adjusts the position of the camshaft
relative to the crankshaft, allowing for precise control of valve timing.
2 Actuator: An actuator, often hydraulic or electronic, is responsible for adjusting the camshaft position
according to signals from the engine control unit (ECU).
3 Sensors: Sensors monitor engine parameters such as RPM, throttle position, and load to determine the
optimal timing adjustments.
Advantages:
1 Improved Performance: VVT enables engines to operate more efficiently across a broader range of RPMs,
resulting in improved horsepower and torque.
60
CITS : Automotive - Mechanic Diesel - Lesson 11 - 14