Page 120 - WCS - Electrical
P. 120
WORKSHOP CALCULATION & SCIENCE - CITS
Uses of Bar Charts
Comparing data across different categories or groups. Showing trends over time by plotting data points at regular
intervals. Highlighting the distribution or frequency of values within a category.
Creating a Bar Chart
Determine the categories or groups you want to compare. Choose a suitable scale for the axes based on the
range of values. Draw bars for each category, ensuring they are proportional to the values they represent.
Label the bars and axes for clarity.
Interpreting a Bar Chart
Compare the lengths of the bars to understand the relative sizes of the categories. Look for patterns or trends in
the data, such as increasing or decreasing values over time. Use the chart to make informed decisions or draw
conclusions based on the data presented. Bar charts are versatile and widely used in various fields, including
business, education, and research, to visually represent data and facilitate easy interpretation.
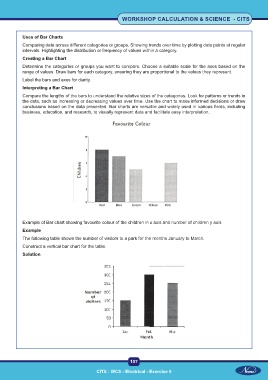
Example of Bar chart showing favourite colour of the children in x axis and number of children y axis
Example
The following table shows the number of visitors to a park for the months January to March.
Construct a vertical bar chart for the table.
Solution
107
CITS : WCS - Electrical - Exercise 9